
Bird’s eye view
In this article, you will be going to learn the Naive Bayes algorithm easily and after this, you can also talk to anyone about this like an expert.
Algorithm
It is the algorithm that is working on the Bayes theorem which describes the method to find the probability of an action or event based on prior knowledge.
For example, a ball may be considered to be a ball if it is round, and about 5 inches in diameter. As we can see these features may describe the ball but these features are independent while contributing that ball is a ball. That’s why we call it a NAIVE.
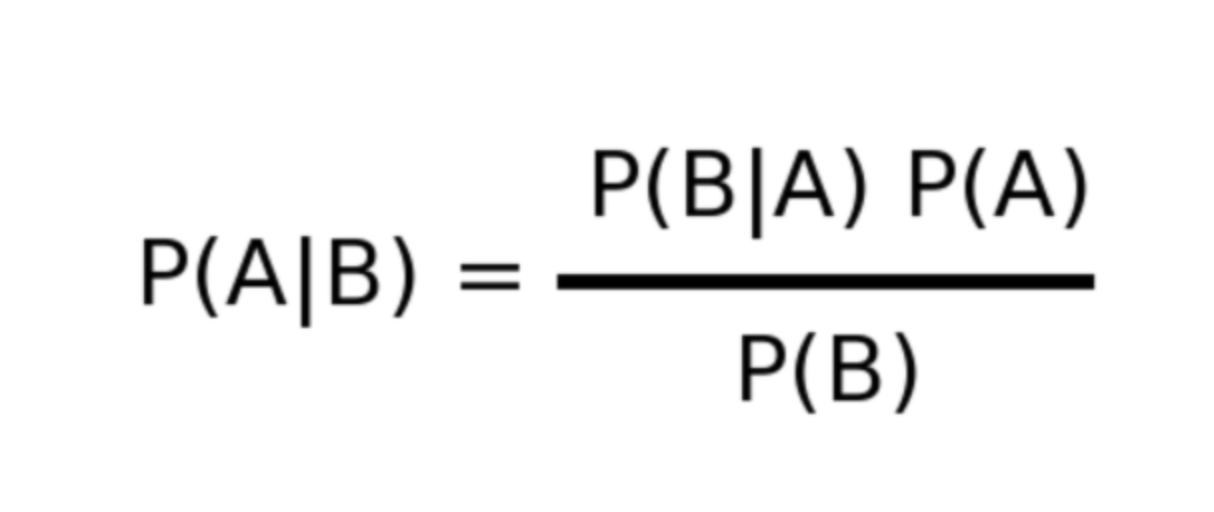
How it works
All you have to do is you just have to convert the data you have into the frequencies for all the classes and have to compute the probability of each case possible then you have to apply the Bayes theorem for prediction as simple as this. As you can see you just have to apply the formulae.
When you should use this
Suppose a situation comes, where you have to classify the data points into some classes and you know that there are too many points then easy way or you can say at sudden I will prefer you to do it by naive Bayes algorithm because it is too fast then others classification algorithm.

Comments
Post a Comment